-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Put all BD® AbSeq Reagents to be pooled into a Latch Rack for 500 µL Tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat. No. 4900). Arrange the tubes so that they can be easily uncapped and re-capped with an 8-Channel Screw Cap Tube Capper (Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat. No. 4105MAT) and the reagents aliquoted with a multi-channel pipette.
BD® AbSeq tubes should be centrifuged for ≥ 30 seconds at 400 × g to ensure removal of any content in the cap/tube threads prior to the first opening.
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended volume per test. Typical use is 2 µl for 1 × 10^6 cells in a 200-µl staining reaction.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please refer to bd.com/genomics-resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Illumina is a trademark of Illumina, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For U.S. patents that may apply, see bd.com/patents.
Companion Products
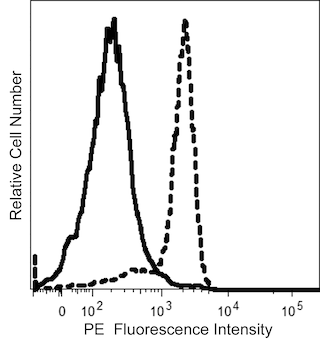




The TU66 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes human CD39 which is also known as Ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 (NTPDase 1), Ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase 1 (Ecto-ATPDase 1), or Ecto-apyrase. CD39 is an integral membrane glycoprotein with two transmembrane domains, N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic tails, and an extracellular region that contains the NTPDase 1 active site. CD39 is encoded by ENTPD1 which belongs to the ectoenzyme family. CD39 is variably expressed on activated T cells and B cells, regulatory T cells (Treg), dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, and granulocytes. CD39 acts on extracellular nucleoside triphosphates and diphosphates including ATP and ADP that are hydrolyzed into AMP. Through cell surface CD73 (Ecto-5'-nucleotidase), regulatory T cells can act on extracellular AMP to generate immunosuppressive adenosine. CD39 is involved in the control of the extracellular pool of phosphorylated nucleosides, the suppression of inflammation and immunity, and the regulation of platelet activation.
Development References (5)
-
Borsellino G, Kleinewietfeld M, Di Mitri D, et al. Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression.. Blood. 2007. (Biology). View Reference
-
Duensing S, Kirshner H, Atzpodien J. CD39 as a novel marker of in vivo immune activation. Blood. 1994; 83(12):3826-3827. (Biology). View Reference
-
Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:1-1182.
-
Stein H, Lennert K, Mason DY, Liangru S, Ziegler A. Immature sinus histiocytes. Their identification as a novel B-cell population. Am J Pathol. 1984; 117(1):44-52. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Ziegler A, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Stein H, Hadam M. A mAb A54 (Tü 66) recognizing a novel avtivation antigen. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:467-468.
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.