-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and CompBead to ensure that BD Comp beads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
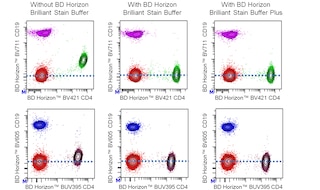
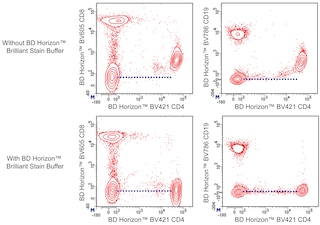
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Product Notices
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 395 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products
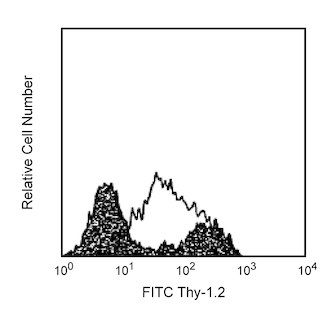



The 37.51 antibody reacts with CD28, which is expressed on most thymocytes, at low density on nearly all CD4+ and CD8+ peripheral T cells, and at even lower density on NK cells. The expression of CD28, in splenocytes and thymocytes, has been reported to increase after activation. CD28 transcripts are found in mast cells, and cell-surface expression of CD28 is induced upon maturation or activation of mast cells. It has been reported that CD28 is not expressed on some populations of intraepithelial T lymphocytes. CD28 is a costimulatory receptor; its ligands include CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). The 37.51 mAb augments proliferation and cytokine production by activated T and NK cells and can provide a costimulatory signal for CTL induction. There is considerable evidence that CD28 is a costimulatory receptor involved in many, but not all, T cell-dependent immune responses.
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV395 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. With an Ex Max near 348 nm and an Em Max near 395 nm, BD Horizon BUV395 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) laser and detected with a 379/28 filter. This dye has been exclusively developed by BD Biosciences as an optimal dye for use on instruments equipped with the ultraviolet laser and has virtually no spillover into any other detector.

Development References (16)
-
Bluestone JA. New perspectives of CD28-B7-mediated T cell costimulation. Immunity. 1995; 2(6):555-559. (Biology: Apoptosis). View Reference
-
Cibotti R, Punt JA, Dash KS, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Surface molecules that drive T cell development in vitro in the absence of thymic epithelium and in the absence of lineage-specific signals. Immunity. 1997; 6(3):245-255. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Gelfanov V, Lai YG, Gelfanova V, Dong JY, Su JP, Liao NS. Differential requirement of CD28 costimulation for activation of murine CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte subsets and lymph node cells. J Immunol. 1995; 155(1):76-82. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Gross JA, Callas E, Allison JP. Identification and distribution of the costimulatory receptor CD28 in the mouse. J Immunol. 1992; 149(2):380-388. (Immunogen: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Harding FA, Allison JP. CD28-B7 interactions allow the induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the absence of exogenous help. J Exp Med. 1993; 177(6):1791-1796. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Inhibition, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP. CD28-mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature. 1992; 356(6370):607-609. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
June CH, Bluestone JA, Nadler LM, Thompson CB. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994; 15(7):321-331. (Biology). View Reference
-
Krummel MF, Allison JP. CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J Exp Med. 1995; 182(2):459-465. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Lepesant H, Pierres M, Naquet P. Deficient antigen presentation by thymic epithelial cells reveals differential induction of T cell clone effector functions by CD28-mediated costimulation. Cell Immunol. 1995; 161(2):279-287. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Marietta EV, Weis JJ, Weis JH. CD28 expression by mouse mast cells is modulated by lipopolysaccharide and outer surface protein A lipoprotein from Borrelia burgdorferi. J Immunol. 1997; 159(6):2840-2848. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Nandi D, Gross JA, Allison JP. CD28-mediated costimulation is necessary for optimal proliferation of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 1994; 152(7):3361-3369. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Nishio M, Spielman J, Lee RK, Nelson DL, Podack ER. CD80 (B7.1) and CD54 (intracellular adhesion molecule-1) induce target cell susceptibility to promiscuous cytotoxic T cell lysis. J Immunol. 1996; 157(10):4347-4353. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ong CJ, Lim AS, Teh HS. CD28-induced cytokine production and proliferation by thymocytes are differentially regulated by the p59fyn tyrosine kinase. J Immunol. 1997; 159(5):2169-2176. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Rakasz E, Hagen M, Sandor M, Lynch RG. Gamma delta T cells of the murine vagina: T cell response in vivo in the absence of the expression of CD2 and CD28 molecules. Int Immunol. 1997; 9(1):161-167. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Shahinian A, Pfeffer K, Lee KP, et al. Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science. 1993; 261(5121):609-612. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wells AD, Gudmundsdottir H, Turka LA. Following the fate of individual T cells throughout activation and clonal expansion. Signals from T cell receptor and CD28 differentially regulate the induction and duration of a proliferative response. J Clin Invest. 1997; 100(12):3173-3183. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Stimulation). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.