-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




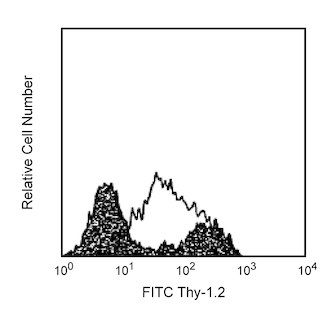
Two color flow cytometric analysis of CD4 expression on mouse splenocytes. Mouse splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/32 antibody (Mouse Fc Block™)(Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with FITC Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e antibody (Cat. No. 553061/553062/561827) and either BD Horizon™ BUV563 Rat IgG2b, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 612925; Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ BUV563 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 antibody (Cat. No. 612923; Right Plot) at 0.5 µg/test. The two-color fluorescence contour plots showing the correlated expression of CD4 (or Ig Isotype Control staining) versus CD3e were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristic of viable splenic leucocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.


BD Horizon™ BUV563 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBead to ensure that BD CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
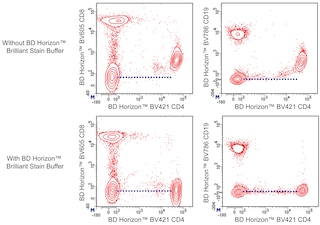
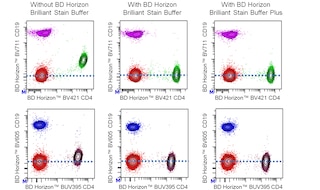
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Note: When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid cell subsets (mature erythrocytes and precursors) has been observed. For researchers studying these cell populations, or in cases where light scatter gating does not adequately exclude these cells from the analysis, this background may be an important factor to consider when selecting reagents for panel(s).
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 563 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The GK1.5 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the mouse CD4 (L3T4) differentiation antigen. CD4 is expressed on most thymocytes, a subpopulation of mature T lymphocytes (i.e., MHC class II-restricted T cells, including most T helper cells), and a subset of NK-T cells. In addition, CD4 has also been reported to be detectable on pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells, bone marrow myeloid and B-lymphocyte precursors, intrathymic lymphoid precursors, and a subset of splenic dendritic cells. CD4 has also been reported to be expressed on the plasma membrane of mouse egg cells and is involved in adhesion of the egg to MHC class II-bearing sperm. CD4 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck. The GK1.5 antibody reportedly blocks binding of the RM4-5 and H129.19, but not RM4-4 mouse CD4-specific antibodies.
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV563 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 which has an Ex Max of 348 nm and an acceptor dye. The tandem has an Em Max at 563 nm. BD Horizon BUV563 can be excited by the 355 nm ultraviolet laser. On instruments with a 561 nm Yellow-Green laser, the recommended bandpass filter is 585/15 nm with a 535 nm long pass to minimize laser light leakage. When BD Horizon BUV563 is used with an instrument that does not have a 561 nm laser, a 560/40 nm filter with a 535 nm long pass may be more optimal. Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there may be spillover into the PE and PE-CF594 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.

Development References (10)
-
Bosselut R, Zhang W, Ashe JM, Kopacz JL, Samelson LE, Singer A. Association of the adaptor molecule LAT with CD4 and CD8 coreceptors identifies a new coreceptor function in T cell receptor signal transduction. J Exp Med. 1999; 190(10):1517-1526. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Dialynas DP, Quan ZS, Wall KA, et al. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983; 131(5):2445-2451. (Immunogen: Blocking, Depletion, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Dialynas DP, Wilde DB, Marrack P, et al. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983; 74:29-56. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Depletion, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Frederickson GG, Basch RS. L3T4 antigen expression by hemopoietic precursor cells. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(4):1473-1478. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Ghobrial RR, Boublik M, Winn HJ, Auchincloss H Jr. In vivo use of monoclonal antibodies against murine T cell antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989; 52(3):486-506. (Biology). View Reference
-
Janeway CA Jr. The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992; 10:645-674. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kruisbeek AM. In vivo depletion of CD4- and CD8-specific T cells. Curr Protoc Immunol. 1991; 4.1.1-4.1.5. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity, Depletion). View Reference
-
Wineman JP, Gilmore GL, Gritzmacher C, Torbett BE, Muller-Sieburg CE. CD4 is expressed on murine pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1992; 180(7):1717-1724. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Wu L, Antica M, Johnson GR, Scollay R, Shortman K. Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult mouse thymus. J Exp Med. 1991; 174(6):1617-1627. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zheng B, Han S, Kelsoe G. T helper cells in murine germinal centers are antigen-specific emigrants that downregulate Thy-1. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(3):1083-1091. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.