-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




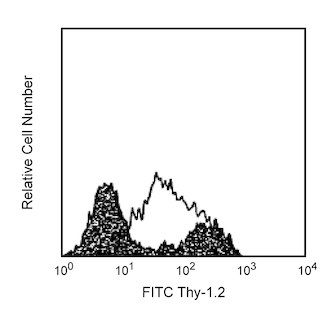
Analysis of ICOS (CD278) Expression Left Panel - Two-color flow cytometric analysis of ICOS (CD278) expression on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Whole blood was stained with APC Mouse Anti-Human CD3 antibody (Cat. No. 555335/561810/561811) and either no antibody (BD Horizon™ BUV395 Autofluorescence Control; Top Plot) or BD Horizon BUV395 Hamster Anti-ICOS (CD278) antibody (Cat. No. 565884/565885; Bottom Plot). Erythrocytes were lysed with BD FACS Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202). Two-color flow cytometric contour plots showing the correlated expression of ICOS (CD278) [or BD Horizon™ BUV395 Autofluorescence] versus CD3 were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes. Right Panel - Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of ICOS (CD278) expression on mouse thymocytes. Mouse thymocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 (Cat. No. 553051/561091) and PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD8a (Cat. No. 553033/553032/561095) antibodies, and either no antibody (BD Horizon BUV395 Autofluorescence Control; dashed line histograms) or BD Horizon BUV395 Hamster Anti-ICOS (CD278) antibody (solid line histograms). The fluorescence histograms showing ICOS (CD278) expression (or BD Horizon™ BUV395 Autofluorescence) were derived from CD4 and CD8 gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable thymocytes as indicated. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.


BD Horizon™ BUV395 Armenian Hamster Anti-ICOS (CD278)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
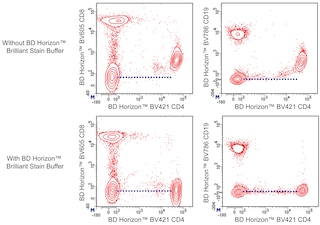
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer should be used anytime BD Horizon Brilliant™ dyes are used in a multicolor flow cytometry panel. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. When BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is used in in the multicolor panel, it should also be used in the corresponding compensation controls for all dyes to achieve the most accurate compensation. For the most accurate compensation, compensation controls created with either cells or beads should be exposed to BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer for the same length of time as the corresponding multicolor panel. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The C398.4A monoclonal antibody specifically binds to Inducible Costimulator (ICOS), which is also known as, CD278, Activation-inducible lymphocyte immunomediatory molecule (AILIM), or H4. ICOS is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that forms a disulfide-linked homodimer and belongs to the CD28 family within the Ig superfamily. ICOS is expressed on either CD4+ or CD8+ single-positive mature thymocytes, T cells, or subsets of Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILC). Its expression is upregulated on activated T lymphocytes. ICOS is a costimulatory receptor that can bind to the B7-H2 ligand (CD275, ICOS-L) that is expressed on B cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and endothelial cells. ICOS plays a critical role in many types of T cell-dependent immunity. In the case of humoral immunity, for example, ICOS signaling is critical for the differentiation of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells and development of germinal centers. Although C398.4A was generated against mouse ICOS, this antibody reportedly crossreacts with human, rhesus, and rat ICOS.

Development References (11)
-
Araujo LM, Fert I, Jouhault Q, et al. Increased production of interleukin-17 over interleukin-10 by treg cells implicates inducible costimulator molecule in experimental spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2014; 66(9):2412-2422. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Brenchley JM, Vinton C, Tabb B, et al. Differential infection patterns of CD4+ T cells and lymphoid tissue viral burden distinguish progressive and nonprogressive lentiviral infections.. Blood. 2012; 120(20):4172-81. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Buonfiglio D, Bragardo M, Bonissoni S, et al. Characterization of a novel human surface molecule selectively expressed by mature thymocytes, activated T cells and subsets of T cell lymphomas. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29(9):2863-2879. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Buonfiglio D, Bragardo M, Redoglia V, et al. The T cell activation molecule H4 and the CD28-like molecule ICOS are identical. Eur J Immunol. 2000; 30(12):3463-3467. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Chen Y, Shen S, Gorentla BK, Gao J, Zhong XP. Murine regulatory T cells contain hyperproliferative and death-prone subsets with differential ICOS expression. J Immunol. 2012; 188(4):1698-1707. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Hutloff A, Dittrich AM, Beier KC, et al. ICOS is an inducible T-cell co-stimulator structurally and functionally related to CD28. Nature. 1999; 397(3716):263-266. (Biology). View Reference
-
Klatt NR, Vinton CL, Lynch RM et al. SIV infection of rhesus macaques results in dysfunctional T- and B-cell responses to neo and recall Leishmania major vaccination. Blood. 2011; 118(22):5803-5812. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
McAdam AJ, Chang TT, Lumelsky AE, et al. Mouse inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS) expression is enhanced by CD28 costimulation and regulates differentiation of CD4+ T cells.. J Immunol. 2000; 165(9):5035-40. (Biology). View Reference
-
Redoglia V, Dianzani U, Rojo JM, et al. Characterization of H4: a mouse T lymphocyte activation molecule functionally associated with the CD3/T cell receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(11):2781-2789. (Immunogen: Bioassay, (Co)-stimulation, Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Sonnenberg GF, Mjosberg J, Spits H, Artis D. SnapShot: innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2013; 39(3):622-623. (Biology). View Reference
-
Xu H, Wang X, Lackner AA, Veazey RS. PD-1(HIGH) Follicular CD4 T Helper Cell Subsets Residing in Lymph Node Germinal Centers Correlate with B Cell Maturation and IgG Production in Rhesus Macaques. Front Biosci. 2014; 5(85):1-7. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.