-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




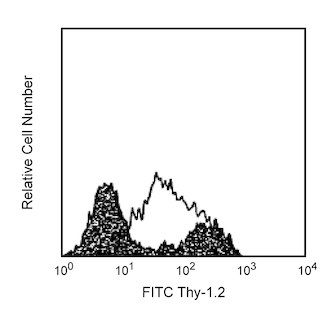
Flow cytometric analysis of CD25 expression on unstimulated and stimulated mouse splenocytes. Left and Middle Panels: Mouse splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 antibody (Cat. No. 553047/553046/561835) and either BD Horizon™ BUV395 Rat IgG1, λ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 564015; Left Panel) or BD Horizon™ BUV395 Rat Anti-Mouse CD25 antibody (Cat. No. 564022; Middle Panel). Two-color flow cytometric dot plots show the correlated expression patterns for CD25 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD4 for events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable splenocytes. Right Panel: Mouse splenic leucocytes were stimulated for 3 days with concanavalin A. The cells were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody and then stained with either BD Horizon™ BUV395 Rat IgG1, λ Isotype Control (dashed line histogram) or BD Horizon™ BUV395 Rat Anti-Mouse CD25 antibody (solid line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphoblasts. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Horizon™ BUV395 Rat Anti-Mouse CD25

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
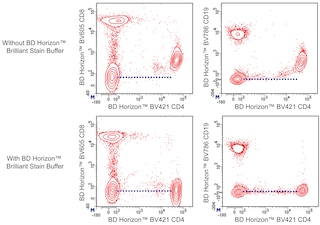
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer should be used anytime BD Horizon Brilliant™ dyes are used in a multicolor flow cytometry panel. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. When BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is used in in the multicolor panel, it should also be used in the corresponding compensation controls for all dyes to achieve the most accurate compensation. For the most accurate compensation, compensation controls created with either cells or beads should be exposed to BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer for the same length of time as the corresponding multicolor panel. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 395 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




The PC61 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD25, the low-affinity IL-2 Receptor α chain (IL-2Rα, p55) expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes from all mouse strains tested. IL-2Rα by itself is not a signaling receptor. However, it can combine with IL-2 Receptor β (CD122) and γc (CD132) chains to form high-affinity, signaling receptor complexes for IL-2. Resting T and B lymphocytes and resting and activated NK cells do not express IL-2Rα. CD25 is transiently expressed at a low level during normal B-cell development in the bone marrow on the CD45R/B220low TdT- sIg- Pre-B/Pre-B-II and CD45R/B220low TdT- sIgM+ sIgD- immature B stages, but not on the CD45R/B220low TdT+ sIg- Pro-B/Pre-B-I stage nor on CD45R/B220high TdT- sIgM+ sIgD+ mature B cells. It is expressed at a higher level during a very early stage of T-cell development in fetal and adult thymus. Peripheral CD25+CD4+ lymphocytes called regulatory T (Treg) cells are involved in the maintenance of self-tolerance. It has also been reported that dendritic cells express CD25, recognized by mAb 7D4. The PC61 antibody recognizes an epitope of CD25 which is distinct from the IL-2 binding site and from those recognized by mAbs 3C7 and 7D4. It blocks binding of IL-2 to CD25, presumably by inducing a conformational change in CD25.

Development References (9)
-
Ceredig R, Lowenthal JW, Nabholz M, MacDonald HR. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985; 314(6006):98-100. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Chen J, Ma A, Young F, Alt FW. IL-2 receptor alpha chain expression during early B lymphocyte differentiation. Int Immunol. 1994; 6(8):1265-1268. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ernst DN, Weigle WO, McQuitty DN, Rothermel AL, Hobbs MV. Stimulation of murine T cell subsets with anti-CD3 antibody. Age-related defects in the expression of early activation molecules. J Immunol. 1989; 142(5):1413-1421. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Garni-Wagner BA, Witte PL, Tutt MM, et al. Natural killer cells in the thymus. Studies in mice with severe combined immune deficiency. J Immunol. 1990; 144(3):796-803. (Biology). View Reference
-
Godfrey DI, Zlotnik A. Control points in early T-cell development. Immunol Today. 1993; 14(11):547-553. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lowenthal JW, Corthésy P, Tougne C, Lees R, MacDonald HR, Nabholz M. High and low affinity IL 2 receptors: analysis by IL 2 dissociation rate and reactivity with monoclonal anti-receptor antibody PC61. J Immunol. 1985; 135(6):3988-3994. (Immunogen: Bioassay, Blocking, Functional assay, Inhibition, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Lowenthal JW, Zubler RH, Nabholz M, MacDonald HR. Similarities between interleukin-2 receptor number and affinity on activated B and T lymphocytes. Nature. 1985; 315(6021):669-672. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Moreau JL, Nabholz M, Diamantstein T, Malek T, Shevach E, Theze J. Monoclonal antibodies identify three epitope clusters on the mouse p55 subunit of the interleukin 2 receptor: relationship to the interleukin 2-binding site. Eur J Immunol. 1987; 17(7):929-935. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Read S, Malmstrom V, Powrie F. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 2000; 192(2):295-302. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.