-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




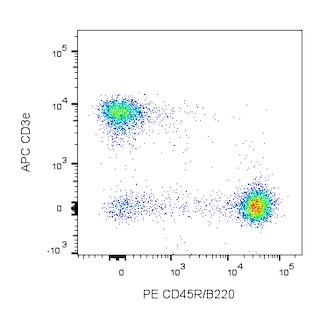
Two-color analysis of the expression of CD40 on mouse spleen cells. BALB/c splenocytes were simultaneously stained with PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD45R/B220 (Cat. No. 553089/553090) and Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD40 (Cat. No. 553721; right panel), followed by FITC Mouse Anti-Armenian Hamster IgM (Cat. No. 553721). Two-color contour plots were derived from gated events with the side and forward light-scattering characteristics of viable splenocytes. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified NA/LE Hamster Anti-Mouse CD40

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For immunohistochemical staining of mouse tissue, we recommend the use Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD40 (clone 3/23; Cat. No. 550285) in our special formulation for immunohistochemistry.
Note: This product may appear to contain aggregation and/or precipitation of the IgM antibody. Investigators are advised to briefly spin down any
particulate matter.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Although hamster immunoglobulin isotypes have not been well defined, BD Biosciences Pharmingen has grouped Armenian and Syrian hamster IgG monoclonal antibodies according to their reactivity with a panel of mouse anti-hamster IgG mAbs. A table of the hamster IgG groups, Reactivity of Mouse Anti-Hamster Ig mAbs, may be viewed at http://www.bdbiosciences.com/documents/hamster_chart_11x17.pdf.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products

.png?imwidth=320)


The HM40-3 antibody reacts with CD40, a 40-50-kDa glycoprotein expressed on B lymphocytes and other antigen-presenting cells. The CD40 molecule has a central role in B-cell growth and differentiation. Furthermore, interactions of CD40 with its ligand, CD154, are involved in the initiation and effector stages of cell-mediated immune responses. CD40 may be involved in the triggering of NK cells and NK-T cells. Soluble HM40-3 antibody stimulates splenic and peritoneal B cells to proliferate in vitro. This antibody also induces spleen B cells to express the costimulatory molecules CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2). HM40-3 mAb has been demonstrated to inhibit the binding of soluble CD154 (gp39, CD40 Ligand) to soluble CD40 and to cell-surface CD40. This hamster mAb to a mouse leukocyte antigen has been observed to cross-react with similar populations of Lewis, Sprague-Dawley, and LOU16 rat leukocytes.
Development References (16)
-
Akiba H, Oshima H, Takeda K, et al. CD28-independent costimulation of T cells by OX40 ligand and CD70 on activated B cells. J Immunol. 1999; 162(12):7058-7066. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Foy TM, Laman JD, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A, Claassen E, Noelle RJ. gp39-CD40 interactions are essential for germinal center formation and the development of B cell memory. J Exp Med. 1994; 180(1):157-163. (Biology). View Reference
-
Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998; 16:111-135. (Biology). View Reference
-
Inaba K, Witmer-Pack M, Inaba M, et al. The tissue distribution of the B7-2 costimulator in mice: abundant expression on dendritic cells in situ and during maturation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1994; 180(5):1849-1860. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Inaba M, Inaba K, Fukuba Y, et al. Activation of thymic B cells by signals of CD40 molecules plus interleukin-10. Eur J Immunol. 1995; 25(5):1244-1248. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Kaneko Y, Hirose S, Abe M, Yagita H, Okumura K, Shirai T. CD40-mediated stimulation of B1 and B2 cells: implication in autoantibody production in murine lupus. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(12):3061-3065. (Immunogen: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Kashiwada M, Kaneko Y, Yagita H, Okumura K, Takemori T. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases via CD40 is distinct from that stimulated by surface IgM on B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(7):1451-1458. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Kawano T, Cui J, Koezuka Y, et al. CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of valpha14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides. Science. 1997; 278(5343):1626-1629. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Leifeld L, Trautwein C, Dumoulin FL, Manns MP, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U. Enhanced expression of CD80 (B7-1), CD86 (B7-2), and CD40 and their ligands CD28 and CD154 in fulminant hepatic failure. Am J Pathol. 1999; 154(6):1711-1720. (Biology). View Reference
-
Munder M, Mallo M, Eichmann K, Modolell M. Murine macrophages secrete interferon gamma upon combined stimulation with interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18: A novel pathway of autocrine macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1998; 187(12):2103-2108. (Biology). View Reference
-
Noelle RJ, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A. CD40 and its ligand, an essential ligand-receptor pair for thymus-dependent B-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1992; 13(11):431-433. (Biology). View Reference
-
Parry SL, Hasbold J, Holman M, Klaus GG. Hypercross-linking surface IgM or IgD receptors on mature B cells induces apoptosis that is reversed by costimulation with IL-4 and anti-CD40. J Immunol. 1994; 152(6):2821-2829. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. A conditioned dendritic cell can be a temporal bridge between a CD4+ T-helper and a T-killer cell. Nature. 1998; 393(6684):474-478. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Tomura M, Yu WG, Ahn HJ, et al. A novel function of Valpha14+CD4+NKT cells: stimulation of IL-12 production by antigen-presenting cells in the innate immune system. J Immunol. 1999; 163(1):93-101. (Biology). View Reference
-
Trinite B, Voisine C, Yagita H, Josien R. A subset of cytolytic dendritic cells in rat. J Immunol. 2000; 165(8):4202-4208. (Biology). View Reference
-
Turner JG, Rakhmilevich AL, Burdelya L, et al. Anti-CD40 antibody induces antitumor and antimetastatic effects: the role of NK cells. J Immunol. 2001; 166(1):89-94. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.